Everything You Need to Know About Hypothyroidism
While symptoms of hypothyroidism can be similar to those of many medical conditions, they are often subtle and difficult to recognize. To ensure that another medical issue does not cause your symptoms, you should schedule a check-up with a board certified endocrinologist Miami, FL, and a blood test to check your thyroid hormone levels. You likely have another medical condition if your symptoms persist or do not go away after treatment.
Symptoms
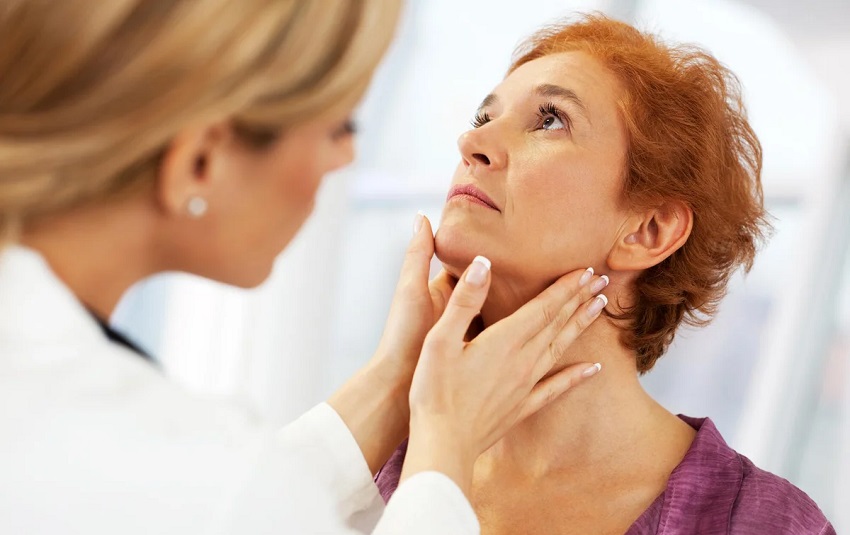
Hypothyroidism is a condition where your thyroid isn’t producing enough thyroid hormones, which can lead to various symptoms. While hypothyroidism symptoms differ from person to person, some common ones include fatigue, cold intolerance, constipation, slow metabolism, and dry skin. Other surprising symptoms can include joint and muscle pain and puffy skin. Your doctor can help you understand the symptoms and determine if you might have the condition.
If you suspect you may be hypothyroid, visit a physician as soon as possible. Hypothyroidism is a potentially life-threatening condition. In addition to affecting your health, your pregnancy may also be at risk. The thyroid hormone plays an essential role in fetal development, and hypothyroidism can severely impact your baby’s development. Children born to hypothyroid mothers typically have a lower IQ and delayed psychomotor development. Still, it’s important to know that women with hypothyroidism can still have healthy babies.
Causes
Thyroid hormones control our metabolism and regulate growth and mood. They are produced by the thyroid gland and secreted into the bloodstream. The thyroid gland is also affected by the pituitary gland, which secretes thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TSH) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). If your thyroid gland is not functioning properly, it will not produce enough hormones to control these processes. Fortunately, this condition is treatable with the help of a replacement thyroid hormone.
The thyroid gland plays an important role in the development of an infant, especially in the womb. Thyroid hormones help develop the nervous system and brain, and when these are affected, they can cause developmental problems in the infant. For example, untreated hypothyroidism during pregnancy can result in miscarriage or preterm labor.
Treatment
Hypothyroidism is a condition that affects the thyroid gland. Although only a small percentage of people develop this condition, it can cause many problems. Treatment is often the key to alleviating the symptoms and returning blood levels of thyroid-stimulating hormones to a normal range.
Hypothyroidism results from a failure of the pituitary gland to release the thyroid-stimulating hormone. The failure is usually caused by a tumor or foreign matter that has invaded the pituitary gland. Hypothyroidism is a serious disorder that can affect all aspects of a person’s life, including a mental state. Severe cases can even lead to a coma.
TSH Test
A TSH test can indicate whether you have an underactive thyroid. It measures the amount of free thyroid hormone in your blood. This hormone is normally found in the blood in the normal range of 0.4 to 4.0 milliunits per liter (mU/L). A TSH level that is higher than this level indicates you may be hypothyroid.
If your TSH level is normal, your thyroid is working properly. However, it is a sign that you may have hypothyroidism if it is too high or too low. In this case, further testing will be necessary.
Weight Gain
Several signs indicate a thyroid problem, including weight gain. However, these symptoms can be similar to other conditions, so a proper diagnosis requires testing for TSH. A physical exam may also reveal an enlarged thyroid gland. In severe cases, an imaging scan of the thyroid may be necessary.
The average person who suffers from hypothyroidism will gain between five and 10 pounds. However, those with severe hypothyroidism may gain up to twenty pounds. Most weight gain is from increased salt retention, but some are due to fat gain. If your weight gain exceeds 20 pounds, you should visit a doctor. In addition, your diet and your physical activity level should be checked.
Menstrual Cycle
Hypothyroidism can have a variety of symptoms, including irregular menstrual cycles. The thyroid is an organ that produces hormones that travel throughout the body, giving instructions to different parts. Thyroid hormone levels can be high or low, confusing the body’s hormonal systems and causing menstrual irregularities. A doctor can tell whether you are hypothyroid by taking a blood test. A woman with hypothyroidism will have an elevated level of TSH (stimulating thyroid hormone) and low free thyroid hormone levels.
A decrease in thyroid hormone levels can affect the pituitary gland and the hypothalamus, which control the hormones. These glands release extra TSH and prolactin to compensate for the decrease in thyroid hormone. It can cause irregular menstrual cycles or heavy bleeding. If a woman has a hypothyroid condition, her period may be heavier or shorter than usual or absent or irregular for up to 3 months. Women with hypothyroidism may also decrease fertility and experience a higher rate of early miscarriage.
Depression
A lack of thyroid hormone, also known as hypothyroidism, can affect a person’s mood. It can also be associated with certain mood disorders, such as bipolar disorder. However, not all hypothyroidism causes clinical depression. However, a person suffering from this disorder is at an increased risk of depression.
Many people experience depression at some point in their lives. It is estimated that one in six people will experience depression in their lifetime. Fortunately, most people who suffer from this condition respond well to treatment. Unfortunately, people who have the more severe type of hypothyroidism are more likely to experience depression.